Capital Budget: Understanding The Role and Process in Financial Management
Bookkeeping
Capital Budget: Understanding The Role and Process in Financial Management

It requires considering factors such as exchange rate risk, political risk, and different tax and regulatory environments. The profitability index also involves converting the regular estimated future cash inflows using a discount rate, which is mostly the WACC % for the business. Then, the sum of these present values of the future cash inflows is compared with the initial investment, and thus, the profitability index is obtained. The internal rate of return (or expected return on a project) is the discount rate that would result in a net present value of zero.
Capital Budgeting: Definitions, Steps & Techniques
However, the numbers used in post audit should come from the actual or observed data rather than the estimated data. This allows managers to perform a side-by-side comparison of actual and estimated numbers and see how successfully their project has been implemented and is moving forward. For each specific technique, companies have a predetermined set of criteria against which they compare the project’s expected results to make their acceptance or rejection decision. For example, if a company applies NPV technique, It must have a predefined net present value (NPV) that the project must meet or exceed to be an acceptable investment. Similarly, if a company uses payback method, it must have a predetermined period within which the project must recover all of its initial investment. A capital budgeting process must be carried out with extreme care and delicacy because the assets that pass through this process largely impact the company’s future performance and growth.
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
The total capital (long/short term) of a company is used in fixed assets and current assets of the firm. PlanGuru is another software offering comprehensive budgeting and financial forecasting. Its considerable the ins and outs of asset strength lies in flexibility, offering options for both start-ups and established businesses. In addition, it includes an informative analysis dashboard presenting a graphical view of financial metrics.
Payback Period
- Besides, the factors like viability, profitability, and market conditions also play a vital role in the selection of the project.
- Unless capital is constrained, or there are dependencies between projects, in order to maximize the value added to the firm, the firm would accept all projects with positive NPV.
- Its considerable strength lies in flexibility, offering options for both start-ups and established businesses.
- Using the more common capital budgeting decision tools, let us calculate and see which project should be selected over the other.
- Capital budgeting is the process that a business uses to determine which proposed fixed asset purchases it should accept, and which should be declined.
Opportunity costs are the benefits lost because of investment decisions and important to consider when capital budgeting. The time value of money is about the potential rate of return on the investment as well as the reduced purchasing power over time due to inflation. Lastly, the profitability index, also known as the benefit-cost ratio, is the ratio of payoff to investment. It is calculated by dividing the present value of future cash flows by the initial investment cost. If the profitability index is greater than 1, the project is considered profitable.
PlanGuru
For this purpose, they can apply various risk analysis techniques like sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis, risk adjusted discount rate and certainty equivalent cash flow etc. Real options analysis has become important since the 1970s as option pricing models have gotten more sophisticated. The discounted cash flow methods essentially value projects as if they were risky bonds, with the promised cash flows known. But managers will have many choices of how to increase future cash inflows, or to decrease future cash outflows. In other words, managers get to manage the projects – not simply accept or reject them. Real options analysis tries to value the choices – the option value – that the managers will have in the future and adds these values to the NPV.
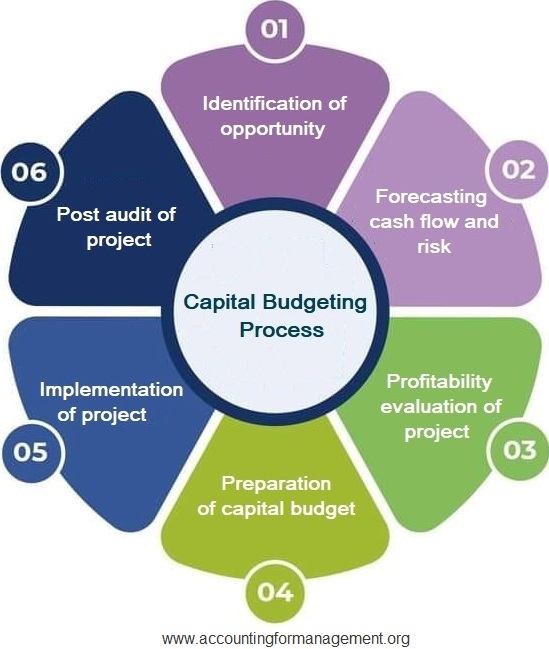
While some are straightforward, others take into account more complex factors such as the time value of money and the risk level of the investment. Therefore, businesses tend to use a combination of these methods when deciding on capital budgeting. Investing in capital assets is determined by how they will affect cash flow in the future, which is what capital budgeting is supposed to do. The capital investment consumes less cash in the future while increasing the amount of cash that enters the business later is preferable. Capital asset management requires a lot of money; therefore, before making such investments, they must do capital budgeting to ensure that the investment will procure profits for the company. The companies must undertake initiatives that will lead to a growth in their profitability and also boost their shareholder’s or investor’s wealth.
Accountants study the impact on profitability and provide required data for decision-making. Capital budgeting is a method of assessing the profitability and appraisal of business projects by comparing their Cash Flow with cost. As mentioned earlier, these are long-term and substantial capital investments, which are made with the intention of increasing profits in the coming years. Choosing the most profitable capital expenditure proposal is a key function of a company’s financial manager. Follow-ups on capital expenditures include checks on the spending itself and the comparison of how close the estimates of cost and returns were to the actual values.
Capital budgeting is part of the larger financial management of a business, focusing on cash flow implications when making an investment decision. Managers will look at how much capital will be spent for a purchase against how much revenue can be generated by the increased output directly related to the purchase. Some of the major advantages of the NPV approach include its overall usefulness and that the NPV provides a direct measure of added profitability. In the two examples below, assuming a discount rate of 10%, project A and project B have respective NPVs of $137,236 and $1,317,856. These results signal that both capital budgeting projects would increase the value of the firm, but if the company only has $1 million to invest at the moment, then project B is superior.

